미래학자
우버 클론 코딩 (nomad coders) #7 본문
노마드 코더 - 우버 클론 코딩
#1.34 Introduction to Twilio
이번에는 휴대폰으로 문자 인증 서비스를 사용하기 위해 Twilio 서비스를 사용할 것이다. 이 서비스는 유료지만 그러게 부담스럽지 않은 가격으로 필요한 인증 서비스를 제공할 것이다.
https://twilio.com 에 접속해서 회원가입을 한 후 번호를 하나 발급 받는데, 꼭 미국 번호로 발급 받아야 한다. 발급 받는데 비용은 $1 다. 이게 어떻게 내는 것인지 잘 모르겠지만,,
https://www.twilio.com/console/sms/settings/geo-permissions 여기서 모든 체크를 해줘야한다. 체크를 안한 국가로는 SMS가 안갈 수 있다.
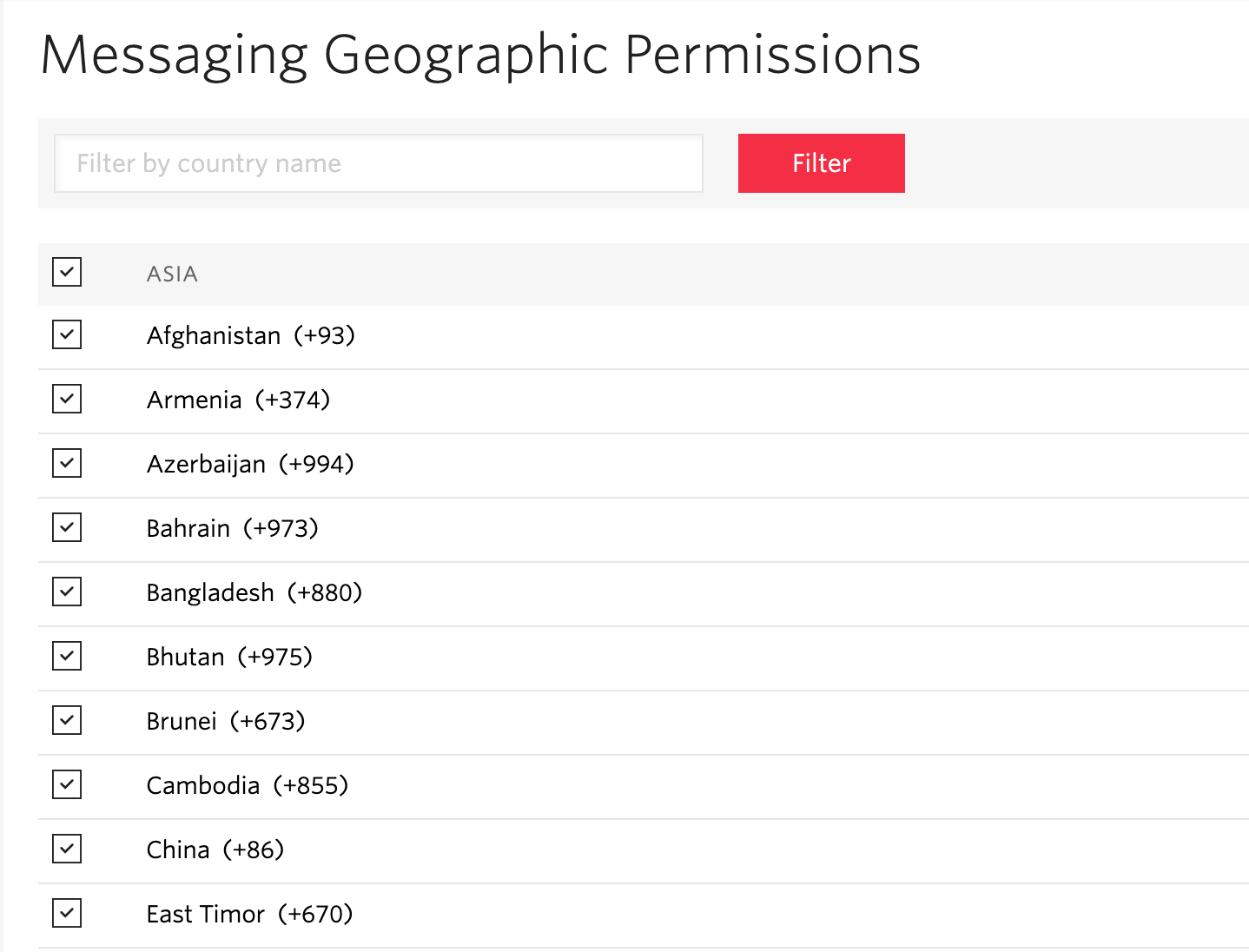
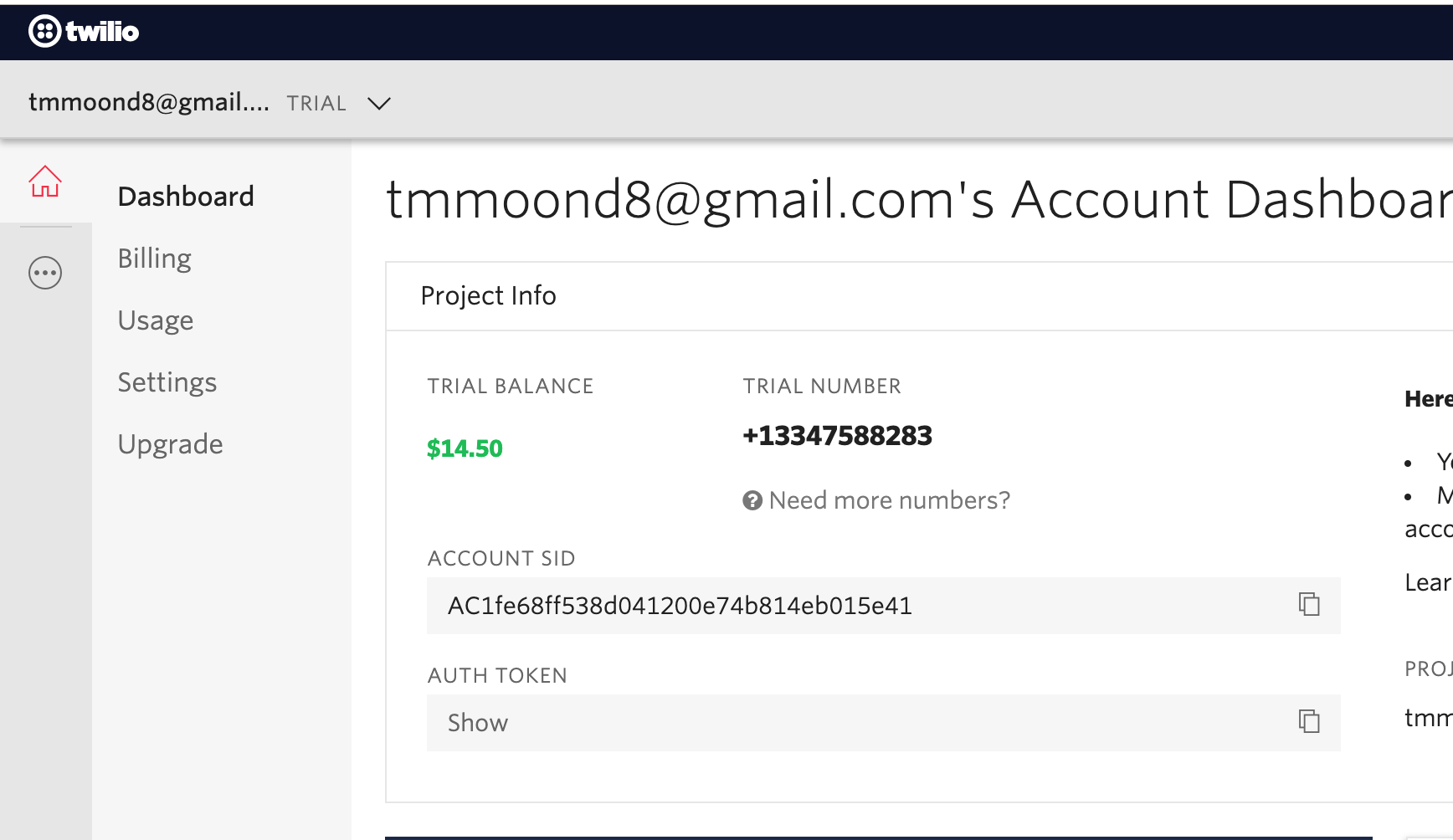
대쉬보드에서 토큰을 확인할 수 있다.
#1.35 StartPhoneVerification Resolver part One
twilio를 통해 폰인증을 구현할 것인데, 앞서 twilio 인증 정보를 .env에 추가하자.
-
src/.env 파일에 TWILIO_SID, TWILIO_PHONE, TWILIO_TOKEN을 추가하자.
... TWILIO_SID=AC1fe68ff538d041200e74b814eb015e41 TWILIO_PHONE=+13347588283 TWILIO_TOKEN=
이번에는 Verification entity에서 User, used를 제거할 것인데, 그 이유는 익명 유저일 때 무언가 문제가 되는 것 같다. used는 사용이 끝난 Verification은 삭제할 것이므로 이 필드가 필요가 없다.
-
src/api/Verification/shared/Verification.graphql
type Verification { id: Int! target: String! payload: String! key: String! createAt: String! updateAt: String } -
src/api/User/shared/User.graphql
type User { id: Int! email: String verifiedEmail: Boolean! firstName: String! lastName: String! age: Int password: String phoneNumber: String verifiedPhoneNumber: Boolean! profilePhoto: String createAt: String! updateAt: String fullName: String chat: Chat messages: [Message] ridesAsPassenger: [Ride] ridesAsDriver: [Ride] isDriving: Boolean! isRiding: Boolean! isTaken: Boolean! lastLng: Float lastLat: Float lastOrientation: Float fbId: String } type Query { user: User } -
src/entities/Verification.ts
import { BaseEntity, BeforeInsert, Column, CreateDateColumn, Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn, UpdateDateColumn, } from 'typeorm' import { verificationTarget } from 'src/types/types'; const PHONE = "PHONE"; const EMAIL = "EMAIL"; @Entity() class Verification extends BaseEntity { @PrimaryGeneratedColumn() id: number; @Column({ type: "text", enum: [EMAIL, PHONE]}) target: verificationTarget; @Column({ type: "text"}) payload: string; @Column({ type: "text"}) key: string; @CreateDateColumn() createAt: string; @UpdateDateColumn() updateAt: string; @BeforeInsert() createKey(): void { if(this.target === PHONE) { this.key = Math.floor(Math.random() * 10000).toString(); } else if(this.target === EMAIL) { this.key = Math.random().toString(36).substr(2); } } } export default Verification; -
src/entities/User.ts
import bcrypt from 'bcrypt'; import { IsEmail } from 'class-validator'; import { BaseEntity, BeforeInsert, BeforeUpdate, Column, CreateDateColumn, Entity, ManyToOne, OneToMany, PrimaryGeneratedColumn, UpdateDateColumn, } from 'typeorm'; import Chat from './Chat'; import Message from './Message'; import Ride from './Ride'; const BCRYPT_ROUNDS = 10; @Entity() class User extends BaseEntity { @PrimaryGeneratedColumn() id: number; @Column({ type: "text", nullable: true}) @IsEmail() email: string | null; @Column({ type: "boolean", default: false}) verifiedEmail: boolean; @Column({ type: "text"}) firstName: string; @Column({ type: "text"}) lastName: string; @Column({ type: "int", nullable: true}) age: number; @Column({ type: "text", nullable: true}) password: string; @Column({ type: "text", nullable: true}) phoneNumber: string; @Column({ type: "boolean", default: false}) verifiedPhoneNumber: boolean; @Column({ type: "text"}) profilePhoto: string; @ManyToOne(type => Chat, chat => chat.participants) chat: Chat; @OneToMany(type => Message, message => message.user) messages: Message[]; @OneToMany(type => Ride, ride => ride.passenger) ridesAsPassenger: Ride[]; @OneToMany(type => Ride, ride => ride.driver) ridesAsDriver: Ride[]; @Column({ type: "boolean", default: false}) isDriving: boolean; @Column({ type: "boolean", default: false}) isRiding: boolean; @Column({ type: "boolean", default: false}) isTaken: boolean; @Column({ type: "double precision", default:0}) lastLng: number; @Column({ type: "double precision", default:0}) lastLat: number; @Column({ type: "double precision", default:0}) lastOrientation: number; @Column({ type: "text", nullable: true}) fbId: string; public comparePassword(password: string): Promise<boolean> { return bcrypt.compare(password, this.password); } get fullName() : string { return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}` } @CreateDateColumn() createAt: string; @UpdateDateColumn() updateAt: string; private hashPassword(password: string): Promise<string> { return bcrypt.hash(password, BCRYPT_ROUNDS); } @BeforeInsert() @BeforeUpdate() async savePassword() : Promise<void> { if(this.password) { const hashedPassword = await this.hashPassword(this.password); this.password = hashedPassword; } } } export default User;
그리고 twilio 모듈을 설치하여 손쉽게 사용하자.
$ yarn add twilio
$ yarn add @types/twilio --dev-
src/api/User/StartPhoneVerification/StartPhoneVerification.graphql
type StartPhoneVerificationResponse { ok: Boolean! error: String } type Mutation { StartPhoneVerification(phoneNumber: String!): StartPhoneVerificationResponse! }graphql type을 생성한 후 yarn types 로 src/types/graph에 추가되도록 하자.
-
src/api/User/StartPhoneVerification/StartPhoneVerification.resolvers.ts
import { Resolvers } from 'src/types/resolvers'; import { StartPhoneVerificationMutationArgs, StartPhoneVerificationResponse } from 'src/types/graph'; import Verification from '../../../entities/Verification'; const resolvers: Resolvers = { Mutation: { StartPhoneVerification: async ( _, args: StartPhoneVerificationMutationArgs ) : Promise<StartPhoneVerificationResponse> => { const { phoneNumber } = args; try { const existingVerification = await Verification.findOne({ payload: phoneNumber }); if(existingVerification) { existingVerification.remove(); } } catch(error) { return { ok: false, error: error.message } } } } } export default resolvers;아직 리턴값을 정의하지않아서 타입 오류가 발생한다. 이건 아래에서 더 채운다.
#1.36 StartPhoneVerification Resolver part Two
-
src/utils/sendSMS 위 강의에 이어서 Twilio로 SMS을 보내는 유틸 파일을 추가할 것이다.
import Twilio from 'twilio'; const { TWILIO_SID, TWILIO_TOKEN, TWILIO_PHONE } = process.env; const twilioClient = Twilio(TWILIO_SID, TWILIO_TOKEN); const snedSMS = (to: string, body: string) => { return twilioClient.messages.create({ body, to, from: TWILIO_PHONE }); }; export const sendVerificationSMS = (to: string, key: string) => snedSMS(to, `Your verification key is : ${key}`);snedSMS: 메시지를 보냄sendVerificationSMS: snedSMS을 이용하여 인증 메시지를 보냄 -
src/api/User/StartPhoneVerification/StartPhoneVerification.resolvers.ts
import { Resolvers } from 'src/types/resolvers'; import { StartPhoneVerificationMutationArgs, StartPhoneVerificationResponse } from 'src/types/graph'; import Verification from '../../../entities/Verification'; import { sendVerificationSMS } from '../../../utils/sendSMS'; const resolvers: Resolvers = { Mutation: { StartPhoneVerification: async ( _, args: StartPhoneVerificationMutationArgs ) : Promise<StartPhoneVerificationResponse> => { const { phoneNumber } = args; try { const existingVerification = await Verification.findOne({ payload: phoneNumber }); if(existingVerification) { existingVerification.remove(); } const newVerification = await Verification.create({ payload: phoneNumber, target: "PHONE" }).save(); await sendVerificationSMS(newVerification.payload, newVerification.key); console.log(newVerification); // 아래에서 확인 후 지울 내용 return { ok: true, error: null } } catch(error) { return { ok: false, error: error.message } } } } } export default resolvers;
자 이제 올바로 메시지를 보내는지 확인해보자.
http://localhost:4000/playground 에서 쿼리를 실행시키자.
mutation {
StartPhoneVerification(phoneNumber: "+82-1033337777") {
ok
error
}
}33337777은 휴대폰 010을 제외한 번호이니 각자 자신의 번호를 대입하면 된다.
올바로 메시지를 보내는 것을 확인하자.
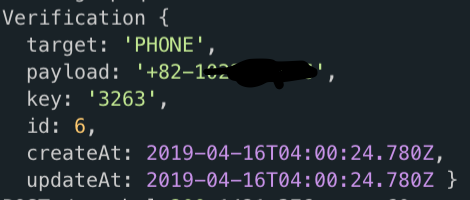
README.md 에서 Start Phone Number Verification 항목을 완료했다.
#1.38 CompletePhoneVerification part One
인증 완료 기능을 진행할 텐데, 먼저 자세하게 어떤 순서로 동작하는지 flow chart가 없어서 설명하는 것이 어렵다. 강의에도 그런 내용이 먼저 나오지는 않는다. 하지만 강의를 좀 더 진행해서 내가 로직을 이해하면 flow chart를 포스팅에 추가하도록 하겠다.
-
src/api/Verification/shared/Verification.graphql 에 verified 필드를 추가하자.
... key: String! verified: Boolean! createAt: String! ... -
src/entities/Verification.ts
... @Column({ type: "text"}) key: string; @Column({ type: "boolean", default: false }) verified: boolean; @CreateDateColumn() createAt: string; ... -
src/api/User/CompletePhoneVerification/CompletePhoneVerification.graphql ComplatePhoneVerification 이라는 mutation과 응답 타입을 정의하자.
type CompletePhoneVerificationResponse { ok: Boolean! error: String token: String } type Mutation { CompletePhoneVerification(phoneNumber: String!, key: String!) : CompletePhoneVerificationResponse! }
#1.38 CompletePhoneVerification part Two
이어서 resolver를 작성하자.
-
src/api/Verification/shared/Verification.resolvers.ts
import Verification from "../../../entities/Verification"; import User from "../../../entities/User"; import { CompletePhoneVerificationResponse, CompletePhoneVerificationMutationArgs } from "src/types/graph"; import { Resolvers } from 'src/types/resolvers'; const resolvers: Resolvers = { Mutation: { CompletePhoneVerification: async ( _, args: CompletePhoneVerificationMutationArgs ) : Promise<CompletePhoneVerificationResponse> => { const { phoneNumber, key } = args; try { const verification = await Verification.findOne({ payload: phoneNumber, key }) if(!verification) { return { ok: false, error: 'Verification token key not valid', token: null } } else { verification.verified = true; verification.save(); } } catch(error) { return { ok: false, error: error.message, token: null } } try { const user = await User.findOne({ phoneNumber }); if(user) { user.verifiedPhoneNumber = true; user.save(); return { ok: true, error: null, token: 'Coming soon' } } else { return { ok: true, error: null, token: null } } } catch(error) { return { ok: false, error: error.message, token: null } } } } } export default resolvers;
이번에는 StartPhoneVerification에 내 폰번를 입력해서 문자를 받은 후에 아래처럼 내 번호와 받은 숫자 4자리를 입력해보자. 잘 입력했다면 ok가 true를 떨어질 것이다. 또 키를 임의의 다른 값으로 바꿔보자. 그러면 false를 리턴하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
mutation {
CompletePhoneVerification(phoneNumber: "+82-1022228888", key: "0000") {
ok
error
}
}README.md에서 Sign Up with Email 항목이 완료됐다.
'nomad corders' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 우버 클론 코딩 (nomad coders) #9 (0) | 2019.04.26 |
|---|---|
| 우버 클론 코딩 (nomad coders) #8 (0) | 2019.04.22 |
| 우버 클론 코딩 (nomad coders) #6 (0) | 2019.04.15 |
| 우버 클론 코딩 (nomad coders) #5 (0) | 2019.04.12 |
| 우버 클론 코딩 (nomad coders) #4 (0) | 2019.04.11 |




